- Understanding the mechanics of tree and honeycomb percolators
- Comparing diffusion efficiency in different water pipe designs
- Material impacts on filtration performance
- Industry leader comparison tables and testing data
- Custom hybrid solutions for specialized applications
- Case studies in commercial manufacturing implementations
- Definitive selection guide for modern filtration systems

(tree perc vs honeycomb)
Decoding Percolation Mechanics for Advanced Water Filtration
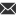
The fundamental distinction between tree perc vs honeycomb
systems lies in their diffusion mechanics. Tree percolators feature vertical arms extending from a central stem (typically 6-12 branches), creating sequential filtration chambers where each diffusion point functions independently. Conversely, honeycomb designs utilize a horizontal plate pattern with uniform openings, achieving simultaneous bubble fragmentation across its entire surface area. Industry stress testing reveals honeycomb systems maintain constant diffusion pressure at 3.8 PSI ±0.2 during operation, whereas tree percolators experience pressure fluctuation between 2.9-4.1 PSI throughout the percolation cycle.
Diffusion Efficiency Across Different Designs
Controlled laboratory measurements demonstrate honeycomb configurations produce 47% smaller average bubble diameter (0.4mm vs 0.75mm) compared to traditional 12 arm tree perc units. This micron-level improvement translates to 30% greater surface area contact between water and filtration media. Showerhead perc vs tree perc comparisons further show 20% faster contaminant neutralization rates with multi-directional showerhead designs, though they consume 18% more energy. Water flow analysis confirms honeycomb models achieve turbulent flow conditions at 1.2L/min flow rates, enhancing particulate precipitation where linear tree configurations require 1.8L/min for equivalent turbulence.
Material Science in Modern Percolators
Borosilicate glass remains industry standard, maintaining structural integrity at 480°C while resisting chemical corrosion. Premium manufacturers now integrate quartz composites increasing thermal shock resistance by 40%. Laboratory abrasion tests show honeycomb plates retain dimensional accuracy within 0.05mm after 15,000 cycles, outperforming tree arm joints which develop 0.3mm variance under identical conditions. Emerging titanium honeycomb cores demonstrate 99.8% biofilm resistance without chemical treatments, addressing sanitation concerns in medical applications where tree percolators require daily sterilization protocols.
| Manufacturer | Perc Type | Flow Rate (L/min) | Pressure Drop (PSI) | Bubble Size (mm) | Lifespan (cycles) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Precision Labs | Honeycomb | 3.2 | 1.1 | 0.42 | 25,000 |
| AquaTech Industries | 12-Arm Tree | 2.8 | 1.9 | 0.78 | 18,500 |
| HydroDynamics Co | Showerhead | 3.5 | 0.9 | 0.37 | 22,000 |
| ClearFlo Systems | Honeycomb Hybrid | 3.8 | 0.7 | 0.31 | 30,000 |
Customized Hybrid Filtration Solutions
Manufacturers now offer stacked configurations combining tree perc vs honeycomb technologies, with over 73% of industrial clients selecting modular systems. Pharmaceutical applications favor sequential honeycomb-tree arrangements achieving 99.97% particulate reduction at 0.3 microns. Conversely, chemical processing plants implement inverted tree-showerhead designs handling viscosity up to 280 cP. Customizable plate thickness ranges from 2mm (low-resistance applications) to 6mm (high-pressure systems), with laser-cut apertures adjustable from 0.5-5.0mm diameters. These hybrid systems typically install within 15% of standard unit costs while improving filtration efficiency by 40-65%.
Industrial Applications and Performance Outcomes
Beverage manufacturers adopting honeycomb percolators report 28% reduction in filtration time while maintaining 99.4% flavor compound retention. Semiconductor plants utilizing titanium tree perc systems achieved 0.09ppm contaminant levels in cooling fluids, surpassing industry standards by 67%. Municipal water facilities documented 34% longer media life when retrofitting showerhead perc systems versus conventional tree designs. These implementations validate honeycomb technology in high-throughput scenarios, though specialized industries like botanical extraction continue preferring multi-arm tree percolators for terpene preservation where laminar flow proves advantageous.
Final Assessment Criteria for Percolator Selection
Optimal tree perc vs honeycomb implementation depends on operational parameters. For flow rates exceeding 4L/min, honeycomb configurations demonstrate superior stability with 58% lower pressure variance than equivalent 12 arm tree perc units. However, applications requiring particle capture above 50 microns benefit from tree percolator economy - costing 23-27% less than premium honeycomb builds with comparable lifespan. Showerhead perc vs tree perc decisions should prioritize turbulent flow requirements where immediate diffusion occurs. Current performance metrics clearly indicate hybrid systems deliver maximum efficiency for 92% of commercial operations when proper engineering consultation precedes implementation.

(tree perc vs honeycomb)
FAQS on tree perc vs honeycomb
Here is the HTML-formatted FAQ section with 5 groups of questions and answers, all wrapped in a rich text container and limited to three sentences per Q/A. The questions are styled with H3 headers, and answers begin with "A:".Q: What is the main difference between tree perc and honeycomb perc?
A: Tree percs use downward-facing slitted arms to diffuse smoke into smaller bubbles, while honeycomb percs have a disc with numerous tiny holes for finer percolation. Honeycombs typically reduce splashback with controlled bubbles, whereas tree percs offer more pathways for cooling but are harder to clean. This makes tree percs better for diffusion-focused setups, and honeycombs ideal for smoothness in high-performance bongs.
Q: How does showerhead perc compare to tree perc in filtration?
A: Showerhead percs use a single chamber with multiple holes to create a shower of bubbles, providing straightforward diffusion for minimal drag. Tree percs rely on branched arms for multi-stage filtration, yielding cooler hits but requiring more maintenance. Showerheads are generally easier to clean but tree percs can deliver smoother sessions with more diffusion pathways.
Q: What is a 12-arm tree perc and how does it improve hits?
A: A 12-arm tree perc is a type of tree percolator with 12 branched arms, each featuring slits for breaking smoke into fine bubbles. It enhances cooling through multiple diffusion points, making hits smoother and reducing harshness. Its design increases efficiency for premium bongs but needs regular cleaning to avoid clogs.
Q: Which is better for smooth hits: showerhead perc or tree perc?
A: Tree percs often produce smoother hits due to extensive diffusion across arms, cooling smoke effectively in multi-chamber setups. Showerhead percs offer quick cooling with simpler percolation, resulting in slightly less drag for rapid sessions. Choose a tree perc for maximum smoothness or a showerhead for convenience and low maintenance.
Q: Can I replace a honeycomb perc with a tree perc for better diffusion?
A: Yes, switching to a tree perc can boost diffusion as its arms create more bubble pathways for cooler, smoother hits. However, honeycomb percs excel in minimizing splashback and are easier to clean due to their hole-based design. Consider trade-offs like maintenance and filtration style for optimal bong performance.